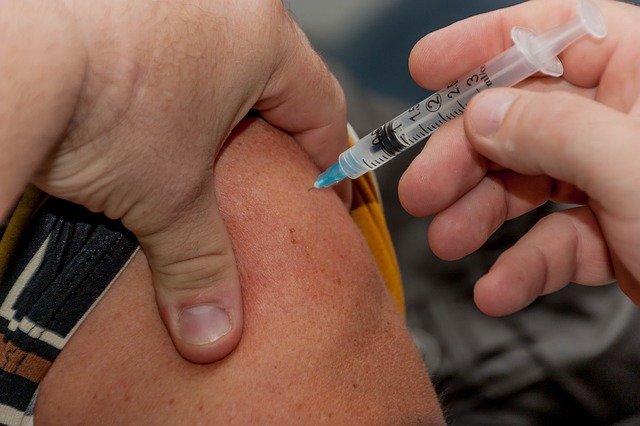
What Is a DNA Vaccine?
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is genetic material found inside the cells of every living organism. You could think of it as an instruction booklet for how cells reproduce themselves in your body.
Since the 1990s, experts have been researching how they could use DNA to create vaccines. These are called DNA vaccines.
How Does the DNA Vaccine Work?
When you get a DNA vaccine, your cells translate the gene particle from the virus or bacteria into a protein that your body recognizes as a foreign element. Your immune system then creates antibodies that fight these particular proteins, stop them from attaching to your cells, and eventually destroy them. The vaccines teach your body to recognize these proteins to prevent future infections.